Information Security in IS
The information system and its dimensions
Security in information systems
Technical Information Security
Preventing DoS attacks
Preventing intrusions
Preventing theft of projects or documents
Preventing identity theft
Preventing DDoS attacks
Firewall
Antivirus, anti-spam, anti-phishing, anti-banner
Proactive defense
Legal Information Security
Protection of individuals regarding personal data and its use
Rights of citizens and consumers
Digital Administration Code
Document management and preservation
Recognition of the legal value of electronically drafted and transmitted acts
Violation of Copyright
Violation of information systems
Information Security in Public Administration
Minimum measures for ICT security in public administrations
ABSC 1 (CSC 1) Inventory of authorized and unauthorized devices
ABSC 2 (CSC 2) Inventory of authorized and unauthorized software
ABSC 3 (CSC 3) Protecting hardware and software configurations on mobile devices, laptops, workstations, and servers
ABSC 4 (CSC 4) Continuous vulnerability assessment and remediation
ABSC 5 (CSC 5) Appropriate use of administrator privileges
ABSC 8 (CSC 8) Defenses against malware
ABSC 10 (CSC 10) Backup copies
ABSC 13 (CSC 13) Data protection
European Regulation 679/2016
Data Protection Officer (DPO)
Scope
Sanctions
Cybersecurity in information systems
Related topics: Technical Information Security, Legal Information Security
Every organization, in the course of its activities, produces or acquires information that is organized and managed by its information system.
The data and associated information constitute the real assets of this activity, and for this reason, it is necessary to protect them legally, technically, procedurally, and organizationally. For more information on information security within an information system, visit our section on Technical Information Security and Legal Information Security.
The information system and its dimensions
The information system of an organization consists of several dimensions:
- Infrastructure dimension
- Organizational procedures dimension
- Human resources dimension
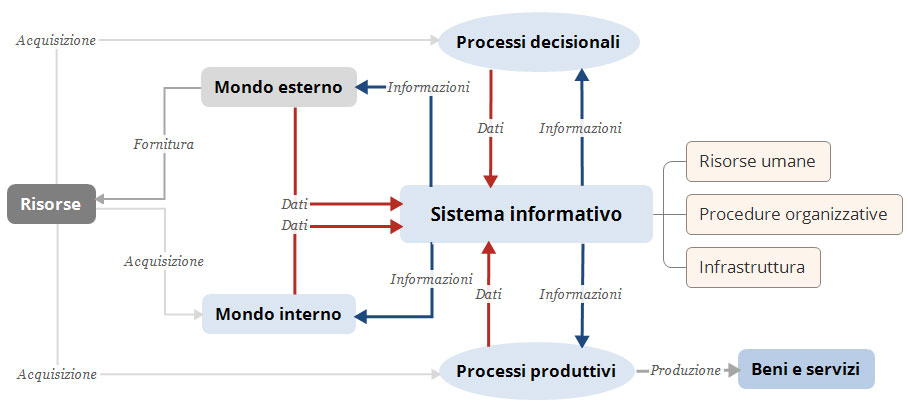
The infrastructure dimension includes the environments where the organization operates and its computer system, which represents the automated part of the information system.
The organizational procedures dimension reflects the organization and management of activities within processes, specifying tasks, functions, and roles necessary for the organization's functioning.
The human resources dimension consists of the individuals who perform their work activities within the organization and utilize information from the information system to carry out their assigned processes.
The evolution of communication systems and the widespread use of information technology have led to the majority of information systems being predominantly computer-based.
Security in information systems
Information systems are not isolated entities: they interact with each other and, more generally, with the external world, exchanging data.
This raises the issue of information security in its broadest sense, concerning the three mentioned dimensions as well as the interaction between information systems.
For more information on the legal aspects related to data and their protection, please refer to the section on Legal Information Security.
For more information on the technical aspects of securing an information system, please refer to the section on Technical Information Security.